Mastering SaaS Migration Strategy for Success
“Transitioning to a SaaS business model today is about future-proofing your product and leveraging opportunities for significant growth. The transition won’t be easy: you must be ready to embrace a more agile and customer-centric approach so that your product continuously delivers value to your subscribers. However, if your SaaS concept can effectively satisfy specific customer needs, I suggest exploring this business model — because the future of software products is SaaS.”
— Nata Shved, COO at Brights
Microsoft, Adobe Creative Cloud, and Slack are the definition of SaaS success stories today, but they actually switched to this business model along the way. Why? Well, a SaaS migration strategy opens a very compelling opportunity for businesses. This way, they can reduce upfront costs, be more agile in response to market demands, and leverage recurring revenue streams thanks to a subscription-based pricing model.
So, if you have a traditional application, how do you make it into a SaaS app? That’s what this article is all about: strategies, challenges, examples of SaaS migration to learn from, and tips from our expert team.
If you wonder why the latter is valuable, here is a brief recap. Our company has been providing SaaS development services for 13+ years, building products like Nova Assure, Signal Intent, and WindowSeat. Our expertise includes consulting SaaS companies, building SaaS products from scratch, optimizing existing ones, and migrating traditional apps.
Keep reading to learn our team’s recommendations on embracing the SaaS migration strategy.
Key takeaways
Businesses decide to migrate from traditional apps to a SaaS business model since it allows them to grow, leverage subscriptions for a continuous and predictable stream, and meet market demands more efficiently.
Before beginning SaaS software migration, it’s crucial to conduct thorough market research to assess customer demand, industry trends, and competitive dynamics to ensure market acceptance.
Transitioning to a SaaS model requires adapting your business’s financial, marketing, legal, and product development strategies to align with the unique demands of SaaS operations.
Continuous product enhancement is necessary to retain customers, provide ongoing value, and justify the recurring payments that are essential to the SaaS business model.
Compliance with regulatory requirements such as GDPR, HIPAA, or PCI DSS is a major consideration in SaaS migration, especially given the increased handling of sensitive customer data.
Nova Assure, SaaS app developed by Brights
Should your business migrate to SaaS?
Switching from a traditional application to a SaaS business model is a very alluring opportunity. Firstly, it has allowed a lot of businesses to grow exponentially. Secondly, with a subscription-based model, you’ll have a continuous and predictable stream of monthly and yearly revenue. Moreover, as you expand your business, you can hire more employees and introduce additional value-added services common for SaaS, such as dedicated support, consulting, implementation services, etc.
However, before you decide to implement SaaS migration, you need to determine whether it’s truly a suitable strategy for your business. Moving to a SaaS business model is not a smooth process — it requires considerable changes to both the product and your company’s strategy and mindset. Here is a checklist of green flags that indicate it makes sense for you to make the shift:

Indicators that your business is ready for migration to SaaS.
Market demand: You see a growing interest in flexible, subscription-based services among your target users.
Strategic readiness: Your business is ready to adapt its financial, marketing, legal, and product development strategies to align with the SaaS model.
Scalability: Your business is prepared to invest in a scalable infrastructure that can handle increased user load.
Customer value: You know how to continuously enhance your product in order to provide ongoing value that justifies recurring payments for users.
Customer support capacity: You have the resources to provide ongoing customer service and support.
Compliance: Your business is equipped to handle the regulatory and compliance requirements of SaaS.
Technology fit: Your existing technology and infrastructure can be adapted to a cloud-based, subscription-driven model.
Further in the article, we’ll get into more detail about how to prepare for the upcoming changes, so if this list doesn’t discourage you — keep reading.
How to choose the right SaaS migration strategy for your product?
There isn’t one universal formula for conducting the migration. Your application is unique, and so is its SaaS migration plan. So, where do you start? First things first, we recommend determining a suitable migration type and a cloud migration strategy.
Choosing the migration type
Cloud providers offer several SaaS migration models for organizations to pick from. Each model offers special advantages to specific businesses, and a well-defined SaaS product roadmap can guide your decision on the most appropriate migration path.
| Siloed migration | In the siloed model, businesses migrate their applications individually to the cloud and treat them as separate projects. While simplifying the migration process, this model poses risks associated with coordinating migrated and non-migrated software. | Best suited for small businesses with isolated apps or minimal integration. |
|---|---|---|
| Layered migration | This migration model prioritizes systems over applications. Organizations can minimize disruption and maintain system integrity by prioritizing critical components and functionalities and considering dependencies between them as they migrate systems in a bundle. | Best suited for organizations with complex, interdependent systems. |
| Data migration | It involves transferring on-premise data to the cloud-based SaaS platform as part of an on-premise migration to SaaS strategy. This model ensures data integrity, consistency, and compliance with regulatory requirements. | Best suited for companies that need to preserve large data volumes. |
| Parallel migration | This type of migration involves managing both on-premise and cloud systems simultaneously. It allows businesses to minimize downtime and validate the SaaS system before they migrate the whole infrastructure. The parallel migration method reduces the risk of disruptions and ensures a smooth transition. | Best suited for businesses that require minimal downtime and risk. |
Choosing the cloud migration strategy
SaaS is the largest cloud computing segment, dominating the market with a projected market volume of $428.78 billion in 2025, so a conversation about SaaS software migration inevitably involves cloud migration.
“The first thing to do before migrating to the cloud is planning and developing a strategy. You need to evaluate which services and data are suited for moving to the cloud, considering application architecture, compliance requirements, and privacy needs. Assessing your current IT infrastructure will help you identify necessary changes and minimize disruptions during the transition.”
— Oleksandr N, DevOps engineers at Brights
Back in 2010, Gartner introduced the concept of R-models migration strategy, providing a framework that would help companies understand whether their apps are suitable for the cloud and how to proceed with the migration. Since then, the methodology has been extended. AWS presented the latest approach — the 7Rs model. These are the SaaS cloud migration strategies we focus on here.

Source: AWS
Retain: With this approach, you keep some applications on-premise, mostly due to regulatory requirements, technical limitations, or because they are not cloud-compatible. The model allows for a hybrid environment where only specific workloads are migrated.
Refactor: Sometimes, to leverage cloud-native capabilities, you need to significantly change the app’s code. That’s what this approach involves. It’s suitable for modernizing legacy applications, getting them ready for features like auto-scaling, serverless computing, and more efficient resource management.
Replatform: Also referred to as “lift, tinker, and shift,” the process requires minimal changes to your application for cloud compatibility. Since it focuses on optimizing the app for cloud infrastructure without altering its core architecture, the strategy strikes a good balance between modernization and simplicity.
Repurchase: The strategy involves replacing the current application with a new, cloud-based solution, in this case a SaaS one. This fits best if the existing software cannot meet the business needs anymore, or when a cloud version is more cost-effective.
Rehost: Also known as “lift and shift,” this approach means moving the applications to the cloud with no or minimal modifications. This is quite a straightforward process of lifting the infrastructure as it is and shifting it to the cloud; hence, it is suitable for those organizations that want a swift transition.
Relocate: The strategy involves moving the infrastructure from on-premise to a cloud environment with the least possible changes. This approach is often part of a broader migration from on-premise to SaaS strategy, typically applied to virtual machines, and provides an easy way to transition workloads to the cloud while maintaining the existing setup.
Retire: Not all apps can or need to be migrated. This approach involves taking the applications that are no longer useful out of service. It streamlines operations by discarding outdated or redundant software and focuses resources on other, more critical applications that can benefit from cloud migration.
How to migrate your existing application to SaaS? Step-by-step instruction
Today, migrating to SaaS is a strategic imperative for businesses that want to stay competitive. However, it involves a lot of planning, testing, and continuous optimization. This guide on how to migrate to SaaS will help you understand the process better — just follow the steps below.

SaaS migration process when implemented by Brights
Step 1: Assess your system before the SaaS transition
The first of the SaaS migration steps is to evaluate your application's architecture and infrastructure and analyze potential obstacles. Start by documenting your current technology stack, dependencies, and integration points. You’ll also need to identify which components are cloud-ready and which may require refactoring or replacement.
Tip: The choice of cloud providers you will use depends on what tools you already utilize. For example, organizations that are deeply integrated with the Windows ecosystem will find it easier to migrate to Azure since it is basically the same environment.
Step 2: Build a SaaS migration plan & architecture roadmap
Based on your assessment, create a detailed migration plan that outlines the sequence and timeline for transitioning each component. Define clear milestones with specific deliverables, assign team roles and responsibilities, and establish success criteria for each phase.
Your roadmap should specify your migration approach: lift-and-shift (moving as-is), refactoring (optimizing for cloud), or rebuilding (redesigning with cloud-native components). Include risk mitigation strategies, rollback procedures, and a communication plan to keep stakeholders informed throughout the process.
Step 3: Set up a secure cloud environment for your SaaS
Working with a cloud environment will be a significant part of your SaaS technology foundation. Setting up an AWS, Azure, or GCP environment, configuring security settings, and supplying necessary services always require an expense. Ensuring your cloud environment meets security and performance standards is extremely important. This is why most organizations rely on a cloud computing expert to set them up.
In this case, Brights is a reliable partner in empowering your cloud potential: cloud computing, DevOps, and IT support. Our team of experts will handle your SaaS migration to the cloud while maintaining high compliance and security standards.
“When choosing a cloud service provider, we recommend considering the two factors.
The first one is complexity and scalability. You need a provider that offers flexibility in resource utilization and the ability to scale depending on your business needs. Hybrid solutions can be practical as they allow you to use both private and public cloud environments.
The second one is cost and contract terms. Providers usually offer various pricing plans, which may include discounts or special offers, so be sure to review these terms carefully if you want to optimize expenses.”
— Oleksandr N, DevOps engineers at Brights
Step 4: Execute SaaS data migration securely
Planning your SaaS data migration is the only way to maintain the safety and integrity of your application. Follow these steps to make sure your data transfer goes smoothly:
Estimate data size and network bandwidth;
Use AWS Snowball, Azure Data Box, or Google Transfer Appliance for large-scale data transfers;
Explore hybrid approaches to hosting data (companies with high-risk data protocols usually prefer storing sensitive data on-premise and other databases on the cloud);
Continuously monitor the data transfer process and optimize performance using cloud monitoring tools like Amazon CloudWatch, Google Cloud Operations Suite, or Azure's Monitor.
Step 5: Deploy your SaaS application in the cloud
After transferring data onto the cloud environment and making sure the migration process went seamlessly, it's time to launch your SaaS application. This process will take several steps:
Install infrastructure components. Set up basic infrastructure components like load balancers, VPCs, and security groups. Create an auto-scaling group of EC2 (AWS) instances behind an Elastic Load Balancer to ensure application availability.
Set up dependencies. Configure web servers and databases to support your SaaS application.
Deploy configuration files and code. By using automation tools like AWS Elastic Beanstalk or CloudFormation, you can simplify the deployment process and ensure correct resource provisioning.
Verify functionality. Test your application to make sure all features function correctly, and communication with the databases and external services is well-established.
Step 6: Conduct performance & security validation
In this phase, focus on ensuring maximum performance for your SaaS application. Begin by checking for functionality, stability, and compatibility across various system components. Mimic different user scenarios to ensure a seamless experience.
Once you identify issues, address all performance blocks, compatibility issues, or functional inconsistencies. Optimize your code, streamline database queries, and allocate resources efficiently to ensure your application works flawlessly.
A crucial part of this phase is scalability and load testing. Try high-user traffic scenarios to evaluate your application's scalability. You can use tools like AWS Load Testing services or Apache JMeter to measure your application's response.
Step 7: Switch traffic and complete SaaS transition
Switching traffic to the cloud is another important step toward ensuring your SaaS application completely transitions from on-premise to the cloud environment. This step allows you to gradually shift users to the new setup, minimizing the risk of disruptions.
To successfully switch traffic to the cloud, we suggest following this routine:
Gradually redirect traffic through DNS configuration;
Closely monitor performance metrics like latency and error rates;
Use tools like AWS Route 53, Azure Traffic Manager, or Google Cloud DNS to manage the transition;
Implement a phased approach to allow for real-time adjustments and minimize risks;
Continuously monitor and test all dependencies, including third-party services and APIs;
Ensure all components work seamlessly in the new cloud environment;
Continue post-migration monitoring to detect any issues that may arise.
Step 8: Ensure post-migration resilience & monitoring
It is imperative to implement backup and recovery procedures, monitor logs and metrics for anomalies, and optimize resource usage.
Following the steps above, you can smoothly migrate your SaaS application to AWS, Azure, or any other cloud platform. However, what is even more important is to set up your SaaS infrastructure in a way that would benefit your business most. Read on to find out how Brights.io can help you leverage your digital potential for your business advantage.
Key challenges of SaaS migration, and how to solve them
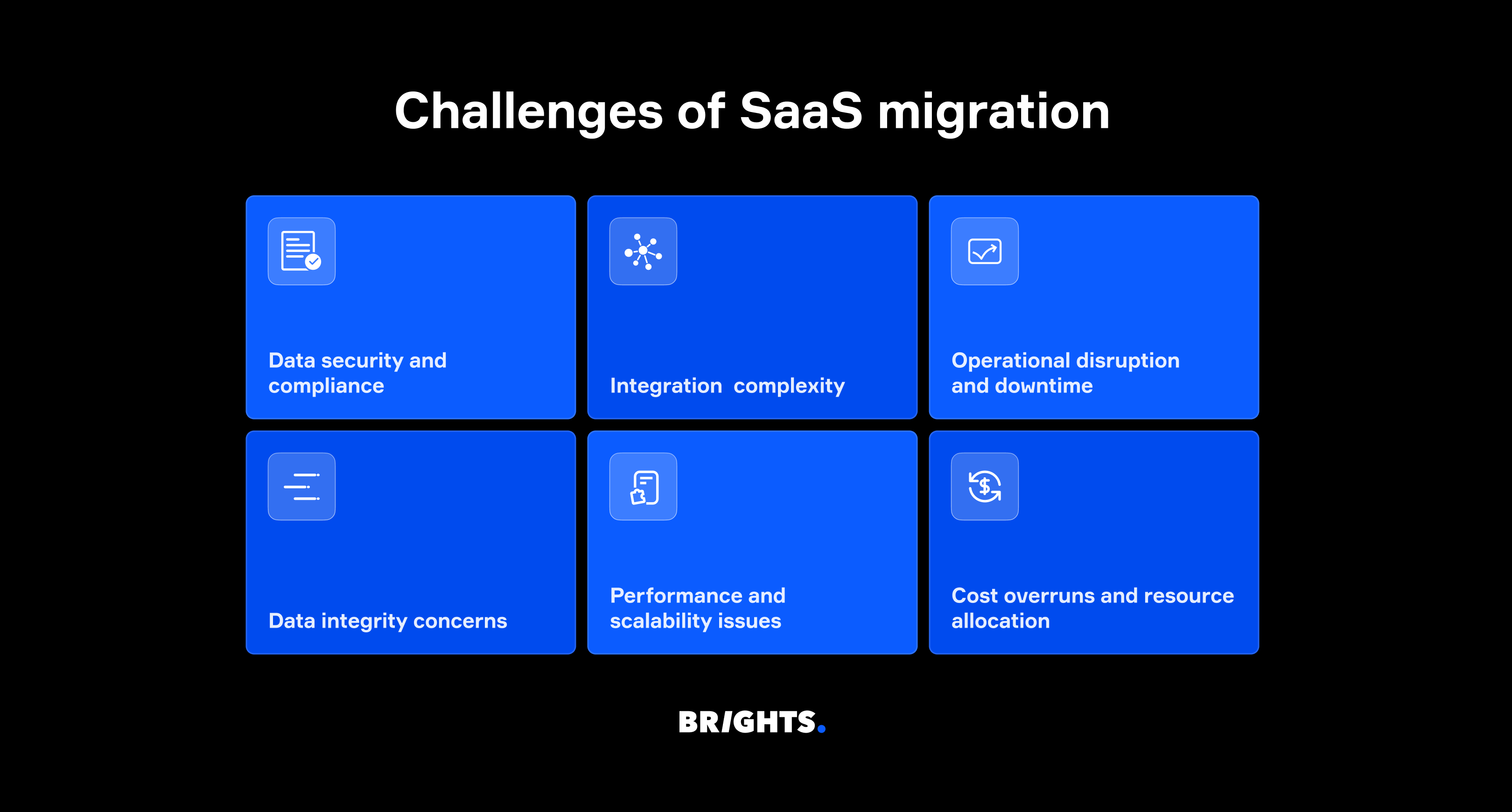
When planning migration SaaS projects, organizations face several interconnected obstacles that require careful navigation. Understanding these typical SaaS software migration challenges upfront helps teams prepare effective mitigation strategies:
Data security and compliance: Protecting sensitive information while meeting multiple regulatory requirements (GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS) across different jurisdictions.
Integration complexity: Ensuring seamless connectivity with existing systems and third-party tools without disrupting workflows.
Operational disruption and downtime: Maintaining business continuity and minimizing service interruptions during the transition.
Data integrity concerns: Preventing data loss, corruption, or inconsistencies throughout the migration process.
Performance and scalability issues: Avoiding system slowdowns and ensuring the new environment can handle current and future demands.
Cost overruns and resource allocation: Managing unexpected expenses and ensuring adequate budget for data transfer, storage, and configuration.
Challenges of SaaS migration
SaaS development solutions often involve storing data across multiple vendors, requiring organizations to comply with different governmental regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS. Making a business comply with all those requirements can be extremely difficult and time-consuming, yet implementing advanced security measures as part of your SaaS migration best practices can help achieve compliance.
Concerns regarding data security arise from the online nature of cloud solutions, which SaaS applications heavily rely on. Organizations must carefully evaluate cloud providers and enforce SaaS security standards (data encryption, access controls, and regular security audits) to protect their sensitive data from potential breaches.
We asked one of Brights’ experts how our team approaches security when migrating software to the cloud.
“We face serious challenges in data security when we migrate to the cloud. To solve them, we use a comprehensive approach that includes compliance with OWASP standards while working on development and architecture. All solutions undergo vulnerability testing using OWASP ZAP and static code analysis. Access to the database is restricted through a special access letter, and access keys are stored only in ENV variables.
Our processes are set up in accordance with ISO 27001 requirements, and we have the corresponding certificate. This includes well-defined backup policies, a Business Continuity Procedure, and a Security Risk Management Procedure, among others. Additionally, all updates are scanned for vulnerabilities before release, and if new CVEs are discovered, we react immediately.”
— Kostiantyn S, QA engineer at Brights
Our engineer also shared that to ensure a timely response and thorough investigation of potential incidents, we employ a complex system of logging, monitoring, and notifications. Our setup includes:
Cloudflare Web Application Firewall to monitor and block suspicious traffic;
Zabbix for monitoring server indicators;
Logging of all security events, including authorization and termination of privileged user sessions;
Application change logging, in particular, to save all user actions in the administrative panel (CRUD);
Sentry for collecting and monitoring errors in the front and backend components of the application;
Firebase Crashlytics for monitoring errors in mobile applications.
When triggers are activated, notifications are automatically sent via Slack, Google Chat, and email. To prevent resource overuse, we configure triggers to alert us during high system loads.
Is your business ready for SaaS migration?
Before starting a SaaS migration journey, businesses should ensure they are ready for the change and transition. While preparing your IT infrastructure is a major part of the process, the changes go far beyond that. So, let’s extend the checklist we’ve gone through at the beginning of this article and see if you’re truly ready for SaaS migration.
Is the market accepting?
In the beginning, your primary task would be to evaluate market demand for SaaS solutions and assess customer preferences. For this, we recommend conducting thorough market research to understand industry trends and your competition.
Here are some of the factors you will have to consider:
Customer demand. Reach out to your existing customers, send out surveys and forms, and conduct interviews. This will help you understand your customers' needs and determine if it is the right time for you to migrate.
Industry trends. Monitor your industry for a shift toward SaaS and cloud-based services. If your competitors are moving in that direction, this indicates market acceptance.
Scalability and flexibility needs. Assess whether your industry increasingly prioritizes scalability and flexibility, which are core benefits of SaaS migration. If so, this might be the right time to transition.
Is your IT infrastructure ready?
Moving to a SaaS business model means you will have to deal with increased infrastructure demands due to higher user loads and security standards since you’ll potentially be handling sensitive customer data. This means that before the migration, you must evaluate your current systems and lay a strong infrastructure basis. Here is what this might include:
Upgrading servers, increasing bandwidth, or adopting cloud-native technologies that can support the scalability and flexibility SaaS requires;
Ensuring your infrastructure can handle increased user loads, provide reliable uptime, and maintain high performance;
Implementing advanced security measures to protect user data, such as strong encryption protocols, firewalls, and compliance with relevant regulations like GDPR or HIPAA;
Deciding between a single-tenant or multi-tenant architecture. Single-tenant is ideal for large enterprises that need dedicated resources, while multi-tenant offers cost-efficiency and scalability for standardized solutions targeting smaller businesses.
Sometimes, the process may get really complicated, especially if the architecture of the existing application is unsuitable for scaling and SaaS in cloud migration. We suggest turning to a tech team with experience in both SaaS development and cloud computing in the beginning for a consultation. This way, you can evaluate the migration complexity and budget needed and make a well-thought-out decision based on that.
Is your business ready?
Before transitioning to a SaaS model, you need to assess whether your business is ready for the change. Start by analyzing the costs involved, including upfront migration expenses, ongoing operational costs, and expected revenue growth. This financial planning should align with your chosen SaaS model and the competitive landscape in your industry.
Additionally, we recommend evaluating your organization's capacity to support and maintain SaaS solutions, considering factors like staffing, training, service level agreements (SLAs), and customer support. Keep in mind that while the ability to scale quickly is a significant advantage, it also demands continuous updates and financial investments. Therefore, it's essential to plan meticulously for ongoing product development.
You can also use questions from the AWS-suggested approach for evaluating your readiness for the SaaS migration:

Source: AWS
Real-world SaaS migration case studies
In addition to learning the theory, we always recommend exploring how it works in a real-life environment and looking for the real-world SaaS migration best practices. Do it not to copy them but to understand what to expect from the market, get inspired, and come up with an approach for your own SaaS implementation.
We’ve recently covered the top SaaS startups to follow, but in this section, we’ll focus specifically on those companies that changed their business model to SaaS along the way.
| Name | How it started | How it’s going |
|---|---|---|
| Autodesk | Autodesk, known for its design and engineering software like AutoCAD, used to sell licenses to access its software in the form of so-called perpetual licenses, which were quite expensive and involved significant upfront investments. The company began migrating to a subscription-only model for its software products starting in 2015. They discontinued perpetual licenses and moved their entire product line to the cloud. | Autodesk incentivized subscriptions for existing customers with discounts, added features, etc. They also highlighted the flexibility that came with this subscription model, allowing customers to scale up or down based on their needs, get automatic updates, and access to software from anywhere. As a result, their customer based accepted the new SaaS model. In 2025, Autodesk announced their total revenue increased 12 percent, reaching $1.64 billion. |
| Adobe Creative Cloud | Adobe's Creative Suite was first sold as a package that a user installed on their computer. However, in 2011, they hit the ceiling, with their yearly sales being flat. In 2013, Adobe switched from selling perpetual licenses of their products (Photoshop, Illustrator, and InDesign) to a subscription-based model where consumers access the software online by paying a monthly or annual subscription fee instead of a one-time purchase. | In the beginning, Adobe gave users an option of buying classic software packages along with switching to a subscription. At the same time, they added more value to the subscription model, adding cloud storage, regular updates, and access to a wider range of applications and services. This helped make the transition easier for users. In 2024, Adobe’s yearly revenue amounted to $21.51 billion. |
| QuickBooks | Founded in 1983, Intuit is famous for QuickBooks, accounting software that was initially available only as a desktop application. Known for adapting to technological shifts, Intuit moved the product to the cloud with QuickBooks Online in 2001 (incredibly early in using cloud technology). The success of QuickBooks Online's success came after a company-wide shift to SaaS, the acquisition of Mint, and significant product updates, including the Harmony update with a simplified setup. | Intuit embraced ratable accounting, where revenue is earned gradually as services are provided, instead of getting it all upfront like traditional software sales. The approach allowed them to launch a simpler version of QuickBooks Online and improve it over time with regular updates. The Harmony update made the software more user-friendly by customizing the setup for different types of businesses, making it less complicated for small business owners. As of 2024, QuickBooks Online had 6.5 million subscribers. |
Why choose Brights as your dedicated migration partner

Testimonial from our client, Michael Alan, founder of Showcase
Throughout our 14+ years in the field, delivering SaaS development outsourcing services have been one of our main areas of work. So, if you're looking for a reliable tech team to migrate your SaaS solution to a custom-built software or transition your product to a SaaS business model, here are a few reasons to consider Brights:
Our company has 120+ bright minds on board, including a strong team of DevOps engineers who specialize in custom-built SaaS software migration. We know how to migrate your web application to SaaS and build scalable mobile SaaS solutions with AWS, GCP, Azure, Heroku, and other trusted cloud providers.
Brights has worked with various B2C and B2B SaaS products, including horizontal solutions that serve diverse users, vertical SaaS tailored to specific sectors, packaged SaaS platforms, and collaborative SaaS apps.
We know how important it is for SaaS companies to build trustworthy relationships with customers by ensuring security, so we make it our priority as well. Brights has ISO/IEC 27001:2013 certification, and we also help our clients get necessary security certifications when needed. In fact, for one of our recent SaaS projects, we helped our client pass an exhaustive security audit and obtain SOC 2 Type II certification for security, availability, and confidentiality.
At Brights, we care about implementing projects that can bring real value to our clients and be worth their investments. If the project doesn’t seem viable, we’ll be upfront with you from the start. But if its potential is backed by our research, we’ll accumulate all our expertise to make your project shine.
Whether you need your technical team enhancement or SaaS consulting, we're committed to delivering solutions that meet your business needs.
Conclusion
We won’t deny that migrating a traditional application to a SaaS business model is lengthy and complicated — you saw that from the step-by-step instructions. Yet we still believe that for businesses with a solid, useful product, it’s a remarkable opportunity to expand. By shifting to SaaS, you can facilitate the continuous evolution of your application, attract new customers, and increase revenue, making it more stable and predictable.
If you decide to explore this opportunity further and implement SaaS migration, don’t hesitate to reach out to our team. From shaping your company’s strategy with a business analyst to getting your application’s infrastructure prepared for the migration, we are here to support you throughout this equally complex and exciting journey.
FAQ.
Most often, SaaS migration involves risks like data loss, downtime, and security vulnerabilities. We mitigate them thorough planning, detailed data migration strategies, choosing a reliable cloud provider, and fundamental data security practices like encryption. Also, we always test the migration process beforehand and prepare a rollback plan in place to secure a smooth transition with minimal disruption.
