Few innovations have been as disruptive, impactful, and recent as the SaaS business model. Whether a startup pivots to embrace this dynamic approach or emerges expressly to leverage its potential, the allure of SaaS revenue in today's bustling market is undeniable. With the aggregated industry value projected to soar past $25 billion annually, seizing the opportunity to delve into the SaaS presents an enticing prospect for organizations of all sizes. Yet, to thrive in this competitive arena, it's imperative to grasp the essence of successful SaaS business model excellence — the strategies, organizational frameworks, and pivotal metrics that underpin business success.
Key takeaways
- SaaS, short for Software as a Service, is a business model where software is hosted on the cloud, enabling users to access its features through monthly or annual subscriptions.
- The SaaS model benefits vendors with predictable revenue, lower upfront costs, and reduced maintenance expenses, alongside scalability, flexibility, and a strategic approach to combat software piracy. It attracts significant investor interest due to its growth potential and high retention rates.
- B2B and B2C SaaS models, while sharing core service and business metrics, differ in focus and strategies. Successful SaaS companies often blend these models, leveraging a dual-funnel strategy to cater to both business clients and individual consumers, enhancing their market reach and profitability.
- There exist six potential pricing options for monetizing your SaaS product: freemium, flat, usage-based, per-user, tiered, and hybrid pricing.
- SaaS founders face challenges such as ensuring data security, managing multi-tenancy complexity, and maintaining regulatory compliance, which are pivotal for sustaining user trust and competitive advantage.
- When bringing your SaaS business model to fruition, you have three primary options: either initiate the project independently and seek software development consulting when needed, assemble an internal team with further augmentation, or opt to outsource the product development process to a third-party service provider.
Why is SaaS taking over the world?
SaaS, or Software as a Service, has swiftly become the preferred choice for both customers and businesses alike. The allure of SaaS lies in its seamless functionality; it simply "just works", without the hassle of installations or the fear of data loss due to hardware failures.
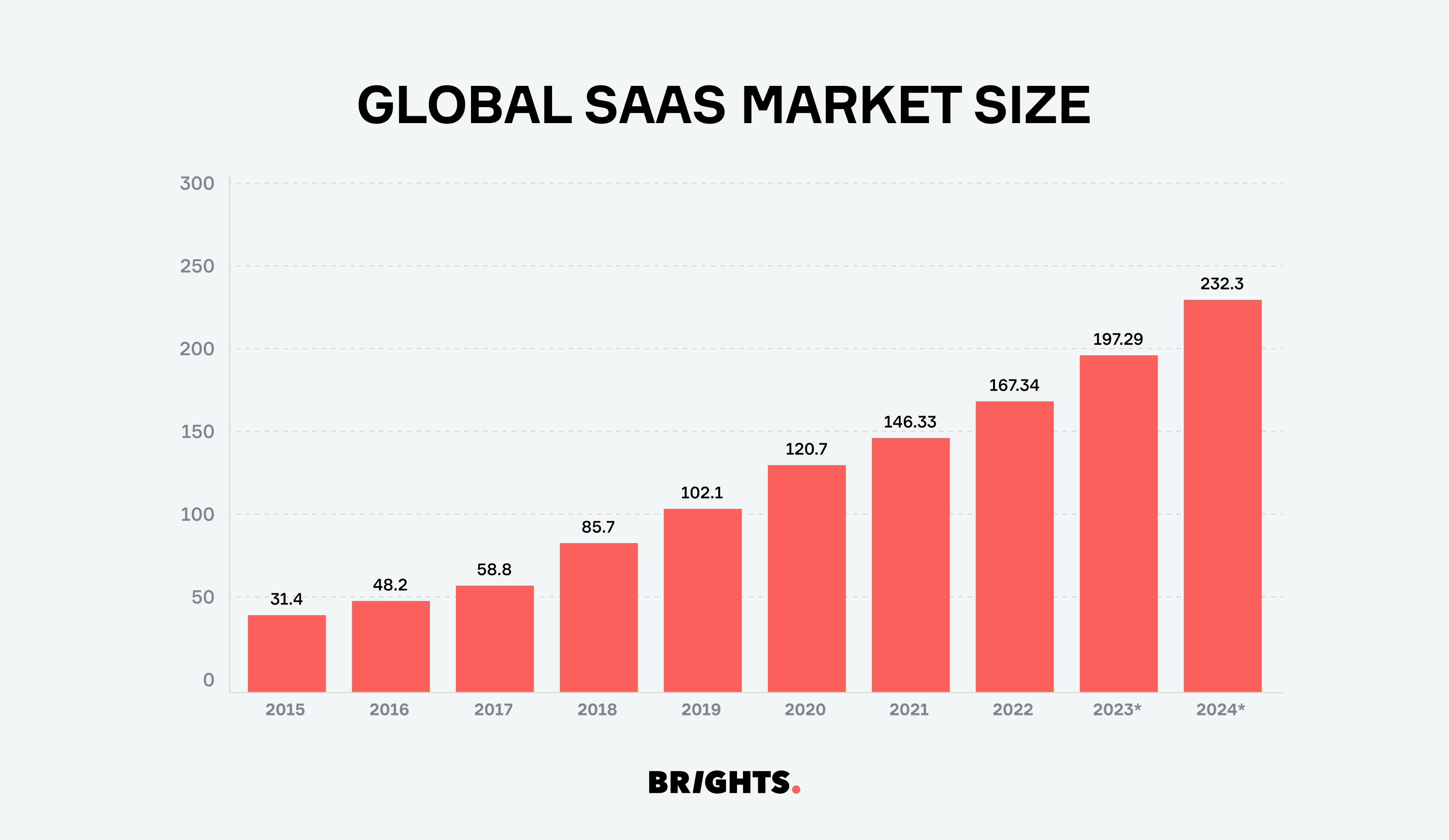
From a business perspective, the economics of SaaS are irresistible, with recurring revenue streams enabling predictable cash flows that fuel rapid expansion. The meteoric rise of SaaS companies, boasting impressive growth rates and a collective industry worth of nearly $197 billion in 2023, underscores their dominance.
SaaS business model in a nutshell
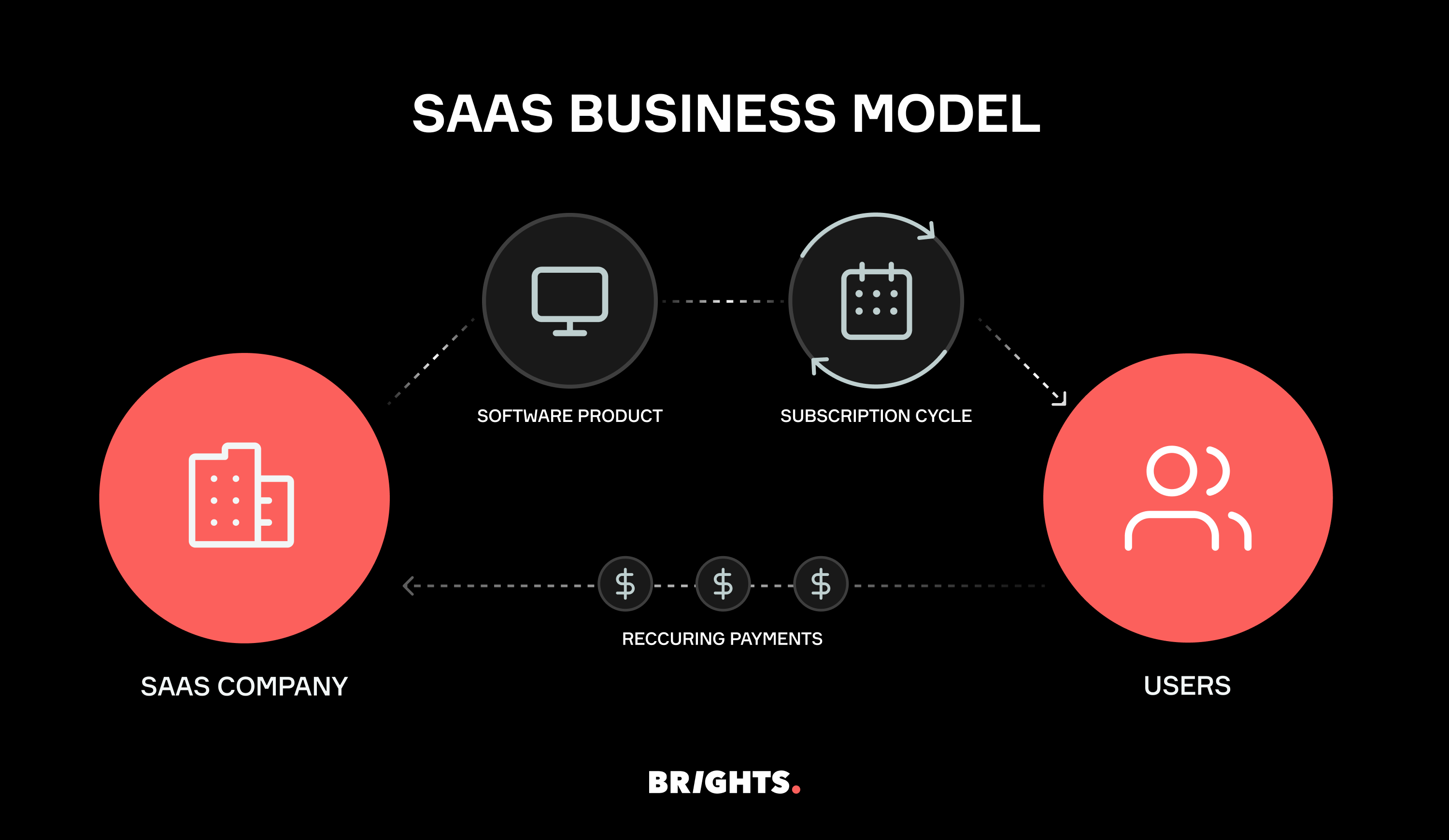
SaaS stands as one of the primary trio of cloud computing service models, sharing the stage with Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) and Platform as a Service (PaaS).
In essence, the Software as a Service business model revolves around financializing software, transforming it from a product with a static price tag into a dynamic, forecastable cash flow instrument. At its core lies a straightforward equation that encapsulates the key metrics driving a SaaS venture's revenue:
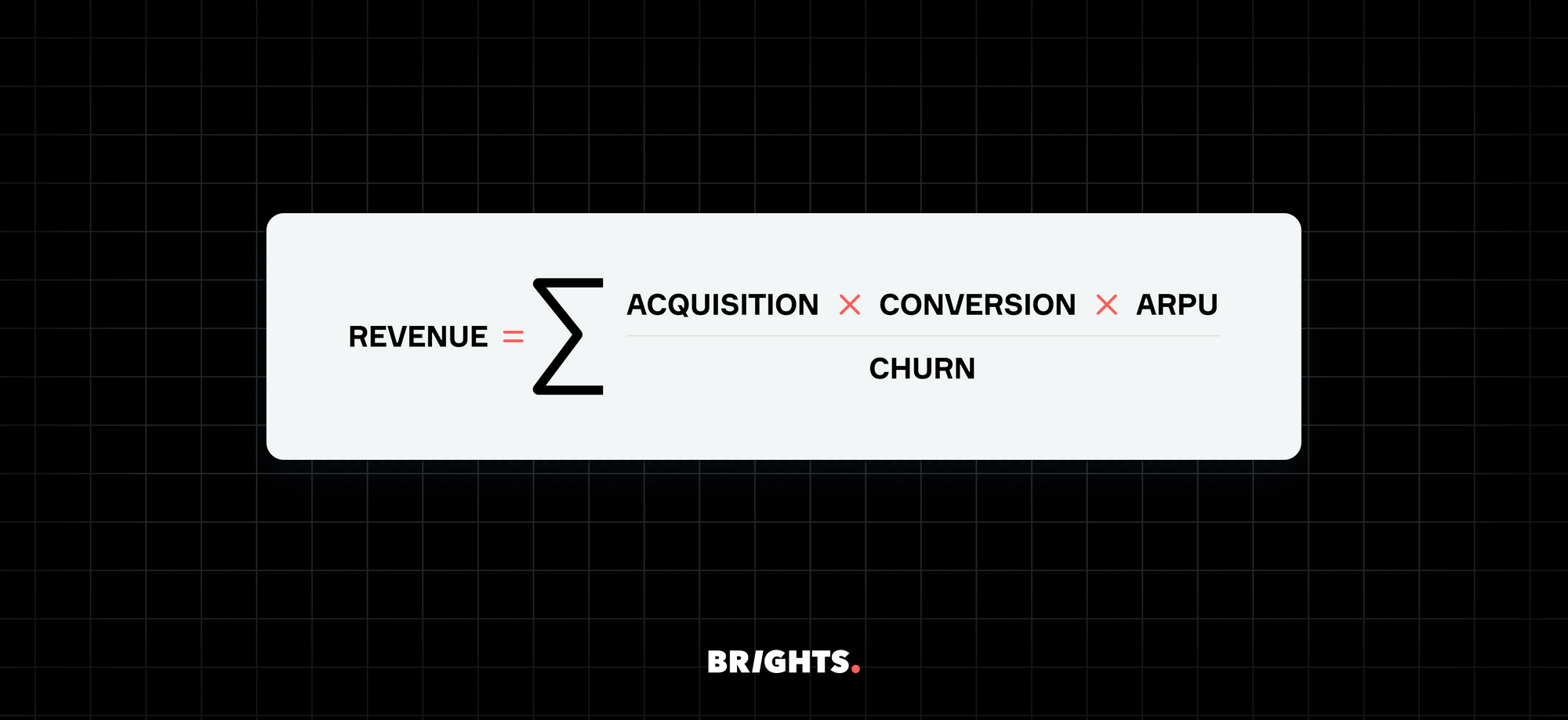
Acquisition represents the effectiveness in attracting and converting prospects into paying customers, while ARPU denotes the average revenue generated per account. Churn, on the other hand, signifies the percentage of customers who discontinue their subscriptions over a given period. By understanding these components and their interplay, businesses can project their long-term revenue and customer lifetime value (LTV) with relative simplicity, facilitating strategic planning and growth.
For instance, imagine a SaaS product with a monthly churn rate of 3%. In this scenario, each customer's expected lifetime would extend to approximately 33 months (1 / 0.03), assuming a steady subscription fee of $50 per month. Consequently, the anticipated lifetime revenue per new customer would total $1,650 ($50 * 33 months).
Furthermore, because SaaS has high profit margins, even small improvements in how many people sign up can lead to immediate increases in revenue and, over time, increase enterprise valuation. While working on getting more customers, keeping them, and reducing the number who unsubscribe might require a lot of effort, changing pricing strategies is a relatively simple way to grow. However, it's important to understand that SaaS companies will approach revenue plateaus, dictated by the interplay of acquisition, conversion, and churn dynamics. If these areas do not improve, growth can stop, putting the company at risk. Especially considering the capital-intensive nature of SaaS expansion, with substantial upfront investments in marketing and sales driving customer acquisition and revenue growth.
Types of software business model
In the software business, various models shape how companies operate and generate revenue. These can be broadly categorized into three main types:
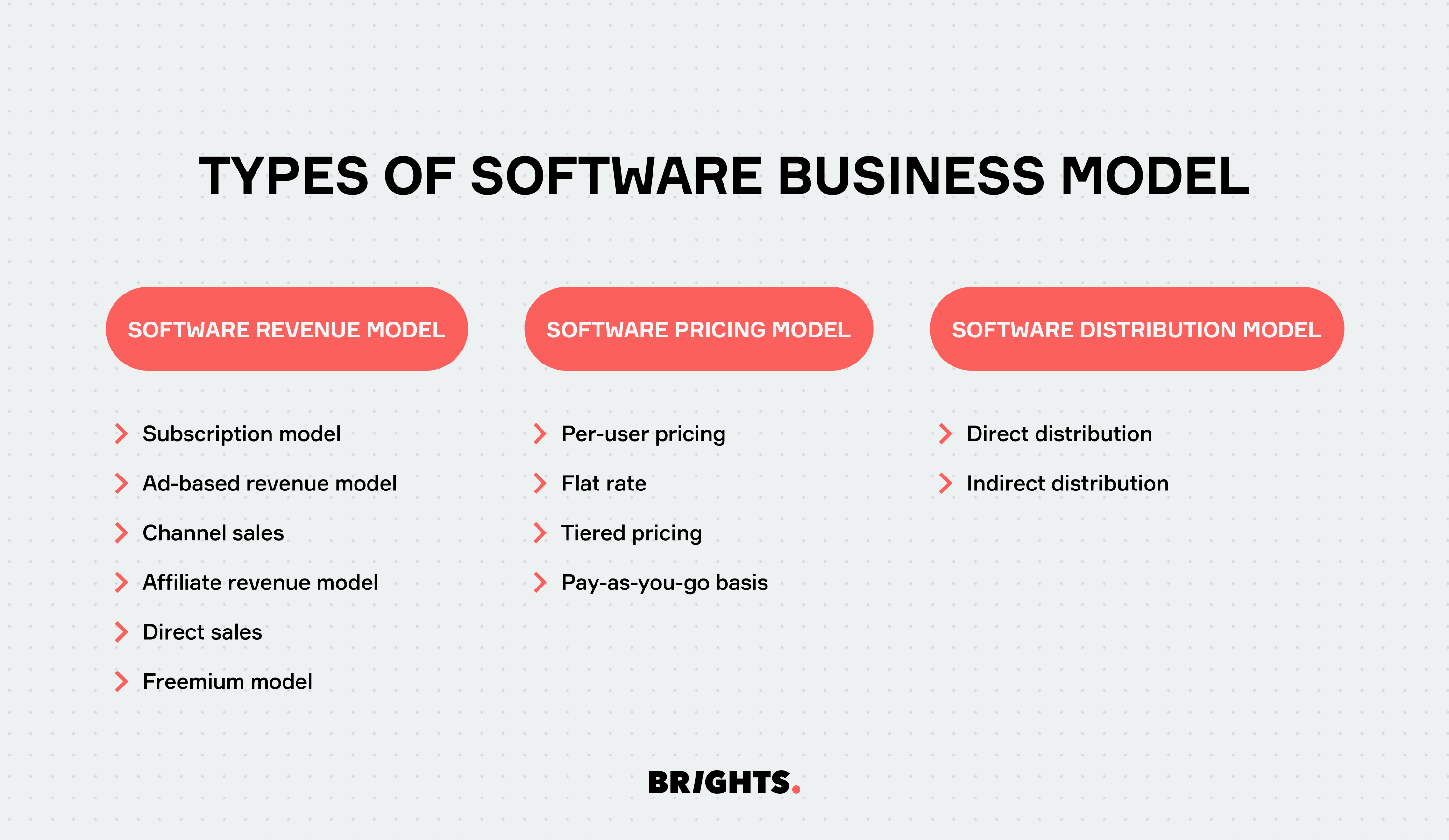
Software revenue model
The software revenue model is pivotal for understanding how a SaaS business generates profit and monetizes its offerings. It not only determines the pricing strategy but also sheds light on the target audience and effective marketing strategies. The following are common types of software revenue models:
- Subscription model
- Ad-based revenue model
- Channel sales
- Affiliate revenue model
- Direct sales
- Freemium model
Software pricing model
In the software pricing model, crucial decisions are made regarding the cost of the service or product. Researching competitors' pricing can offer a competitive edge. Key software pricing models include:
- Per-user pricing
- Flat rate
- Tiered pricing
- Pay-as-you-go basis
Software distribution model
The software distribution model concerns how services or products are disseminated to customers, considering who sells them and the methodologies employed. Common distribution models include:
- Direct distribution
- Indirect distribution
Ultimately, the choice of software distribution model hinges on business requirements, budget constraints, and overarching objectives.
B2B and B2C SaaS models
B2B SaaS and B2C SaaS may share similarities in service provision, business models, and performance metrics, such as churn rate and conversion rate. However, the distinctions between the two are stark, particularly in terms of various departments critical to their operation and success.
| Aspect | B2B SaaS | B2C SaaS |
|---|---|---|
| Development | Targeted at solving specific business challenges | Aimed at personal interests and entertainment |
| Focuses on functionality over mass appeal | Prioritizes user engagement and interface design | |
| Marketing | Emphasizes lead generation and customer engagement | Focuses on emotional connections and brand building |
| Targets logical decision-making processes | Appeals to consumer desires and impulses | |
| Sales | Longer sales cycles due to complex decision-making | Shorter decision-making timelines driven by impulses |
| Involves approval from multiple stakeholders/departments | Decision-making often based on emotions | |
| Customer Service | Addresses complex issues with personalized support | Self-service-oriented approach with online resources |
| Requires prompt handling to build lasting relationships | Efficient resolution through FAQs and tools | |
| Customer Success | Prioritizes personalized relationships and loyalty | Focuses on automated processes for rapid onboarding |
| Relies on emotional connections for retention | Streamlines product adoption for a larger user base |
Many new founders make the mistake of believing they must choose between developing a B2B or B2C SaaS product. However, contrary to this belief, numerous highly profitable SaaS companies successfully operate within both realms simultaneously. They adopt a dual-funnel approach, akin to the strategy exemplified by Dropbox.
Take, for instance, companies like Dropbox, Trello, Canva, Castos, and Squadcast. While primarily categorized as B2B SaaS, they also maintain a substantial consumer or prosumer tier.
Embracing a hybrid model offers significant advantages, including:
- Stable growth curve
By catering to a diverse clientele, you balance smaller customers with higher churn rates alongside businesses at higher price points with lower churn, resulting in a more stable growth trajectory.
- Enhanced brand presence
Engaging with consumers amplifies your brand's reach. A sizable consumer base fosters a strong brand following, facilitating organic word-of-mouth marketing on a larger scale.
- Increased Average Revenue Per User (ARPU)
The varied customer mix typically yields higher ARPU figures compared to traditional B2C SaaS models. Consequently, you can allocate more resources towards sales and marketing initiatives.
Ultimately, there's no definitive answer regarding whether to pursue a B2B or B2C SaaS approach. However, from an economic standpoint, B2B ventures tend to be more advantageous for bootstrapped or predominantly bootstrapped enterprises.
In addition, B2B SaaS solutions typically boast greater complexity and a wider array of features compared to their B2C counterparts. This complexity arises from the distinct requirements of B2B customers, who demand advanced functionalities and customization options tailored to their specific business needs. Moreover, B2B solutions often excel in integration capabilities, security features, and reporting functionalities, among other advanced attributes.
In contrast, B2C SaaS solutions prioritize simplicity and user-friendliness. These solutions emphasize intuitive interfaces and streamlined features to deliver a seamless user experience. While B2C offerings may lack the extensive customization and advanced functionalities of B2B solutions, they excel in accessibility and ease of use, catering to a broader audience.
In essence, success in the SaaS realm hinges on acquiring numerous customers and retaining them, rather than solely focusing on securing large deals.
Examples of successful SaaS platforms
Let's explore a few examples of successful SaaS platforms and delve into how they have transformed their respective industries, catering to both business and consumer needs alike.
LinkedIn stands as a cornerstone in professional networking, revolutionizing the way individuals connect, share insights, and advance their careers. As a B2B SaaS platform, it provides a digital space where professionals can access a suite of services, including job searching, talent recruitment, and professional networking tools. LinkedIn has become an indispensable resource for both professionals and businesses, facilitating meaningful connections and opportunities in the professional landscape.
Slack
As a B2B SaaS communication platform, Slack has redefined workplace collaboration and communication dynamics. Offering features such as instant messaging, file sharing, and seamless integrations with various productivity tools, Slack enables teams to work more efficiently and effectively. Its user-friendly interface and robust functionality have made it a staple in modern workplaces across industries, empowering teams to streamline communication and collaboration processes.
Spotify
Spotify stands out as a transformative force in the realm of music consumption, offering a personalized and immersive music streaming experience. Operating as a B2C SaaS platform, Spotify provides users with access to an extensive library of songs, playlists, and podcasts on-demand through its subscription-based model. With personalized recommendations and curated playlists tailored to individual preferences, Spotify has become the go-to destination for music enthusiasts worldwide, reshaping how people discover, enjoy, and share music.
If you're seeking inspiration, dive into our article highlighting the top SaaS startups to watch in 2024.
SaaS product stages
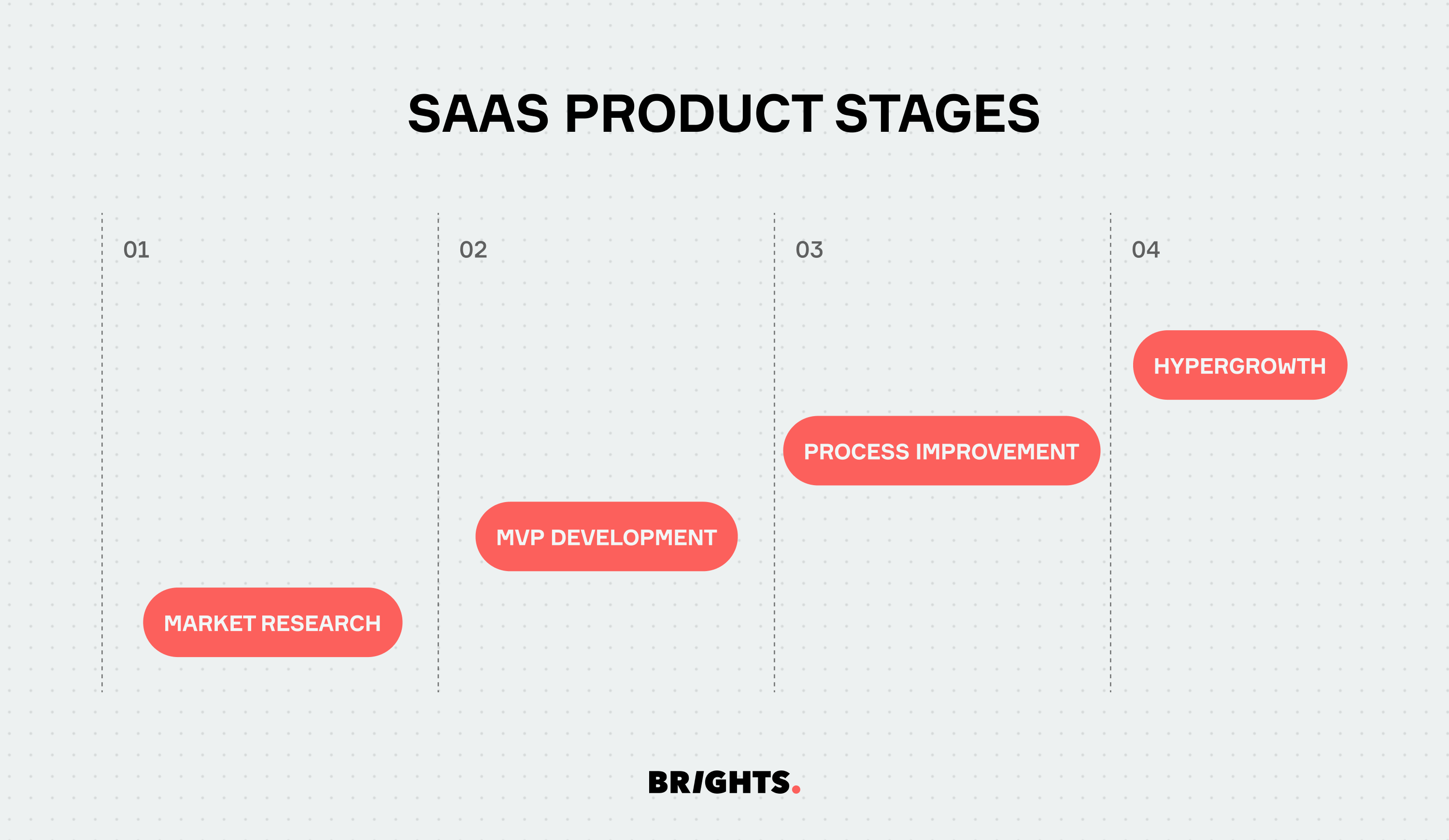
Market research
Market research enables you to understand customer needs, market trends, and competitor landscapes. At Brights, we leverage industry expertise and data-driven insights to identify market opportunities and validate product concepts. With a detailed discovery phase, you gain valuable market intelligence sans development cost, guiding strategic decision-making and maximizing the potential for product success.
MVP development
The development of a Minimum Viable Product is a crucial stage in the SaaS product lifecycle, allowing businesses to validate their ideas and gather feedback from early adopters. Brights specializes in MVP development, leveraging agile methodologies and rapid prototyping to bring concepts to life efficiently and cost-effectively. With our expertise, you can launch MVP quickly and iteratively, minimizing time to market and maximizing resource efficiency in development cost.
Process improvement
Continuous process improvement is essential for optimizing SaaS product performance and enhancing customer satisfaction. We offer process improvement consulting services, conducting thorough assessments and implementing tailored strategies to streamline workflows, enhance scalability, and drive operational excellence.
Hypergrowth
Hypergrowth signifies a phase of rapid expansion and scaling for SaaS businesses, driven by increasing market demand and customer adoption. Brights team provides technical expertise with team extension to support businesses during hypergrowth phases, offering cloud infrastructure management, performance optimization, and scalability planning services. By leveraging Brights' capabilities, businesses can scale their operations seamlessly and sustainably, enabling them to capitalize on growth opportunities and achieve long-term success.
Read also: How much does it cost to develop a SaaS product?
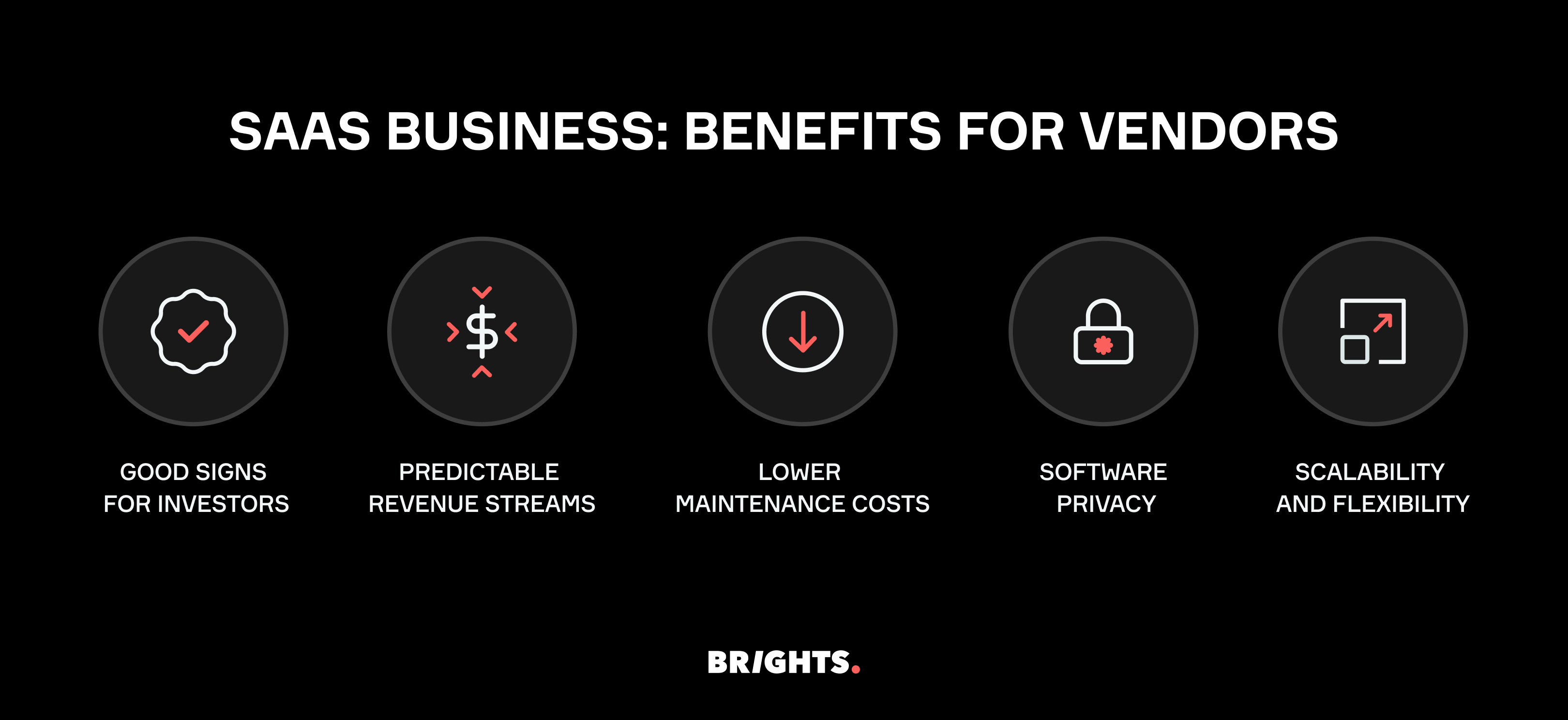
SaaS business: benefits for vendors
Good signs for investors
The subscription-based revenue model, coupled with low customer acquisition costs and high customer retention rates, can lead to exponential revenue growth over time. This growth trajectory is particularly appealing to venture capitalists and private equity firms seeking high returns on investment. According to Dealroom, 47% of VC was invested in startups with a SaaS business model in 2023, a trend that has been on the rise over the past decade. Additionally, the relatively low upfront costs associated with SaaS startups compared to traditional software companies reduce the barrier to entry for investors, allowing for diversification within investment portfolios.
Predictable revenue streams
Advantages of the SaaS business model include vendors' predictable revenue streams, with subscription-based pricing contributing to stable income. According to a report by Gartner, by 2025, SaaS is expected to account for 60% of all public cloud services revenue, highlighting its growing significance as a revenue driver for vendors.
Lower maintenance costs
By leveraging cloud-based infrastructure, SaaS vendors can significantly reduce upfront investment in hardware and IT infrastructure. Research by IDC forecasts that spending on public cloud services will reach $1.35 trillion by 2027, with SaaS accounting for a significant portion of this expenditure, underscoring the cost-saving benefits of cloud-based solutions for vendors.
Software privacy
One effective strategy in combating software piracy involves leveraging the inherent difficulty associated with pirating cloud-based software. Unlike traditional software installations, cloud-based solutions operate on remote servers accessible via the Internet, making unauthorized copying and distribution far more challenging. By adopting cloud-based models, software providers can significantly reduce the prevalence of piracy, safeguarding their intellectual property and revenue streams.
Scalability and flexibility
SaaS platforms provide vendors with scalability and flexibility, allowing them to adapt to changing market demands and user needs. A survey conducted by Flexera found that 93% of organizations reported using SaaS applications, indicating the widespread adoption of SaaS solutions among businesses of all sizes.
Challenges and risks of the SaaS model
Navigating the risks of the SaaS business model poses various challenges that require careful consideration and strategic management.
Multi-tenancy complexity
Multi-tenancy architecture poses intricate challenges in SaaS development, requiring a delicate balance between resource sharing and data privacy, security, and customization. Various models, including isolated, shared, and hybrid tenancy, each present unique complexities that must be navigated effectively to ensure optimal performance and user satisfaction.
Data security and privacy
Data security and privacy are paramount concerns for SaaS development, necessitating robust measures to safeguard sensitive information while maintaining user accessibility and experience. Balancing convenience with comprehensive protection requires careful planning and implementation throughout the SaaS development lifecycle, from design and testing to deployment.
Scalability and performance
Scalability and performance are fundamental considerations in SaaS development, demanding strategies to accommodate growing user bases and maintain seamless operation under varying workloads. Achieving zero downtime deployment, addressing integration challenges, and optimizing system performance are critical for sustaining competitiveness and meeting user expectations.
Integration issues and third-party options
Integration challenges, including third-party integration and data consistency, present significant hurdles for SaaS developers seeking to streamline operations across diverse platforms and applications. Seamless integration of cloud-based SaaS products with other SaaS apps meticulous planning and execution to minimize disruptions and ensure seamless functionality.
Regulatory compliance
Maintaining regulatory compliance is a complex challenge in SaaS development, as companies must navigate a landscape of laws and regulations governing data security, privacy, and financial transactions. Adhering to evolving legal requirements demands ongoing diligence and expertise, ensuring that SaaS solutions meet compliance standards across diverse industries and regions.

Brights SaaS expertise
Our proficiency in SaaS development is exemplified by our involvement in groundbreaking projects such as a creative-focused project management platform aimed at streamlining the production process of creative assets.
In this project we focused on making it easy for users to work with videos and large files. This means they can quickly turn their ideas into real work, and it's also easy to chat and give feedback in real-time now. We also worked on making it simpler to get approval for the work. We designed a system where users can decide how to get things approved. This makes the whole process faster and easier for everyone.
Security was another area where we made a big difference. We added an extra layer of protection, kind of like a secret code, to keep the work safe and make the platform intuitive.
Lastly, we made sharing and getting notifications better. Now, users can share the work with others and get notified instantly. This means they don't have to wait, and can see their work right from the email.
Our partnership has transformed it into a more user-friendly and secure platform, ideal for managing creative projects and working with the team and partners. Brights' contributions underscore the power of successful collaboration in delivering valuable tools for creative teams.
The future of SaaS
In conclusion, the future of SaaS is poised for unprecedented expansion and transformation. As technology evolves and consumer expectations evolve alongside it, the SaaS landscape will continue to evolve rapidly, offering novel solutions to address emerging challenges across industries. With advancements in artificial intelligence, machine learning, and data analytics, the potential for SaaS to revolutionize business operations, streamline workflows, and drive innovation is immense.
Moreover, the rise of edge computing, 5G technology, and the IoT will further propel the growth of SaaS by enabling seamless connectivity and unlocking new use cases. As such, entrepreneurs, developers, and investors alike stand poised to capitalize on the vast opportunities presented by the dynamic and ever-expanding field of SaaS. With the right vision, strategy, and execution, the possibilities are truly limitless in shaping the future of SaaS and redefining the way we work, collaborate, and interact with technology.
